Milk and buttermilk are two dairy products that differ in taste and texture. Are you trying to decide between milk and buttermilk? Both are popular dairy products but have distinct characteristics that set them apart. We will explore the differences between milk and buttermilk, helping you make an informed choice for your recipes and dietary needs. Milk is a versatile and nutritious beverage that is widely consumed worldwide.
It is produced by mammals, such as cows, goats, or sheep, and is rich in essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and vitamins. Milk is smooth and creamy, making it suitable for various culinary uses, from baking to making coffee and tea.
Also Read: Oat vs Soy Milk: Which Plant-Based Milk Is the Healthiest?
On the other hand, buttermilk is a fermented dairy product that is tangier than regular milk. It is made by churning butter from cultured cream, resulting in a tart and slightly thicker liquid. Buttermilk’s distinctive taste makes it popular in recipes like pancakes, biscuits, and salad dressings.
While milk and buttermilk have unique purposes and flavours, the choice between them often depends on personal preference and the recipe requirements. Now that we have introduced these two dairy products let’s delve deeper into their characteristics and discover when it is best to use each one.
Contents
overview of Milk vs Buttermilk
| Aspect | Milk | Buttermilk |
|---|---|---|
| Source | From cows | From cows |
| Production | Raw or pasteurized milk | Cultured buttermilk is made by fermenting milk with lactic acid bacteria, while traditional buttermilk is a byproduct of churning cream to make butter. |
| Texture | Liquid | Thinner than milk, but slightly thicker than yogurt due to fermentation. |
| Taste | Mild, slightly sweet | Tangy, slightly sour |
| Color | White | Can be white or slightly off-white, depending on the fermentation process. |
| Nutritional Content | Good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein. Contains lactose. | Lower in fat compared to milk. Contains probiotics due to fermentation. Still a good source of calcium and protein. Contains less lactose. |
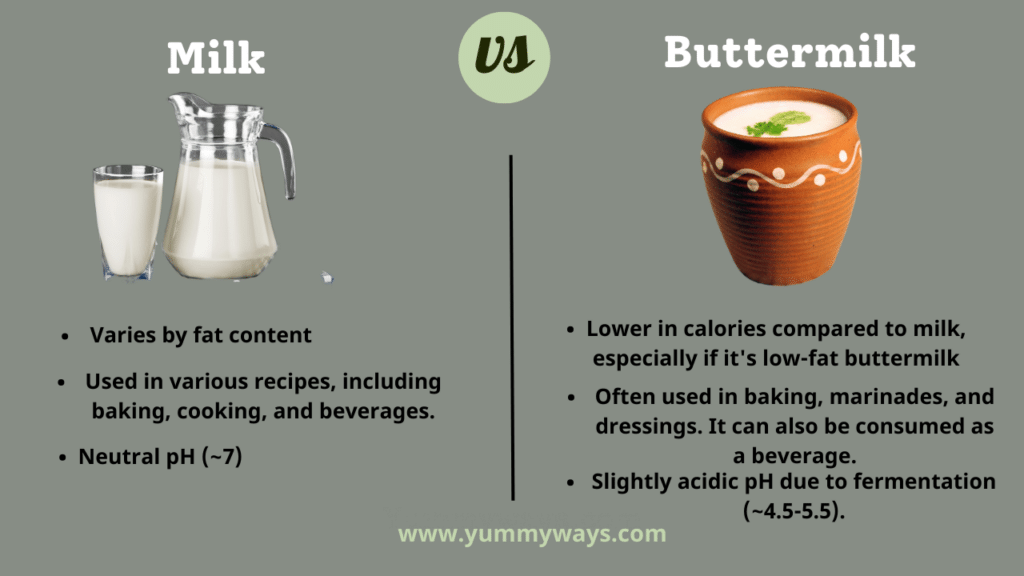
| Calories | Varies by fat content | lower in calories compared to milk, especially if it’s low-fat buttermilk. |
| Uses in Cooking | Used in various recipes including baking, cooking, and beverages. | Often used in baking, marinades, and dressings. It can also be consumed as a beverage. |
| Cultured Varieties | N/A | Cultured buttermilk is intentionally fermented, which gives it a tangy flavor and thicker texture. |
| Lactose Content | Used in various recipes, including baking, cooking, and beverages. | Contains less lactose due to fermentation, making it easier to digest for some people with lactose intolerance. |
| Acidic pH | Neutral pH (~7) | Slightly acidic pH due to fermentation (~4.5-5.5). |
Also Read: Milk vs Yogurt: Which is Better for Your Health
Understanding The Basics
- Nutrient-Milk-Buttermilk
- Calories- 60-41
- Protein-8g-4g
- Fat-3.6g-1g
- Calcium-293mg-370mg
- Vitamin D-2.9mcg-0.8mcg
Milk and buttermilk are dairy products, but they have distinct differences in nutritional composition. Milk contains 60 calories, 8g of protein, 3.6g of fat, 293mg of calcium, and 2.9 mcg of vitamin D per serving. On the other hand, buttermilk has 41 calories, 4g of protein, 1g of fat, 370mg of calcium, and 0.8mcg of vitamin D per serving.
It is important to note that buttermilk is lower in calories, protein, and fat than regular milk; however, it contains slightly higher amounts of calcium. Milk and buttermilk have unique nutritional profiles, so it depends on personal dietary needs and preferences when choosing between them.
Health Benefits And Considerations
Milk and buttermilk are both dairy products known for their health benefits. When comparing the nutrient content, buttermilk is lower in fat and calories than milk. It is also a good protein, calcium, and vitamin D source.
Both milk and buttermilk can aid in digestion and promote gut health. They contain beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut flora. Drinking milk has been associated with lower cholesterol levels, while buttermilk specifically has been shown to help reduce LDL cholesterol.
For those looking to manage their weight, buttermilk can be a better choice as it is lower in calories. It can be used as a substitute for milk in various recipes without compromising taste and texture. Milk, on the other hand, is more suitable for those who do not have weight concerns and can benefit from its higher fat and calorie content.
- Nutrient-Milk-Buttermilk
- Protein-8g-8g
- Fat-8g-2g
- Calcium-280mg-300mg
- Vitamin D-2.5mcg-3mcg
Culinary Uses And Flavor Profiles
Milk versus buttermilk, two dairy products with unique flavour profiles and culinary uses. Milk, a staple ingredient in cooking and baking, is widely used to create creamy sauces, moist cakes, and fluffy pancakes. It adds richness and depth to dishes, enhancing their overall taste. On the other hand, buttermilk, with its tangy and slightly acidic taste, is a popular ingredient in traditional and modern recipes.
Milk is often used in cooking to create creamy soups, rich sauces, and delectable custards. Its smooth texture and mild flavour make it a versatile ingredient, perfect for sweet and savory dishes. Milk is crucial in creating moist and tender cakes, flaky pastries, and soft bread when baking. It adds moisture to the dough and helps in achieving a desirable texture.
With its distinct tanginess, buttermilk is used in baked goods like biscuits, scones, and muffins. Its acidity reacts with leavening agents like baking powder and baking soda, resulting in a lighter and fluffier texture. Moreover, buttermilk’s unique flavour profile complicates sweet and savoury dishes.
Whether you choose milk or buttermilk, both have their place in the culinary world. Their different flavour profiles and versatile uses make them essential ingredients in various recipes.
Also Read: Evaporated Milk vs Powdered Milk: Which is Better for Cooking?
Fermentation Process And Probiotic Content
Milk and buttermilk differ in their fermentation process and probiotic content. Buttermilk is made through the fermentation of milk, usually by adding lactic acid bacteria. This fermentation process gives buttermilk its tangy taste and creamy texture. The probiotic content of buttermilk is higher compared to regular milk.
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for the digestive system. Buttermilk contains probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which can help improve gut health and boost the immune system. These probiotics can also aid in the digestion of lactose, making buttermilk a suitable option for individuals with lactose intolerance.
On the other hand, milk also contains some natural bacteria, but the probiotic content is lower than buttermilk. However, milk is still a good source of essential calcium, protein, and vitamins.
| Buttermilk | Milk |
|---|---|
| It may cause digestive issues for some | Lower probiotic content |
| Tangy taste and creamy texture | Regular taste and texture |
| Suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals | May cause digestive issues for some |
In conclusion, buttermilk’s fermentation process contributes to its higher probiotic content, making it a healthier option than regular milk. However, both milk and buttermilk have their nutritional benefits and can be enjoyed based on personal preferences and dietary needs.
Dairy Alternatives: Milk And Buttermilk Substitutes
Plant-based Milk Alternatives:
Milk alternatives have gained popularity among individuals who are lactose intolerant, allergic to dairy, or following a vegan lifestyle. These plant-based alternatives offer various options with different taste profiles and nutritional benefits.
Almond milk is a popular choice that is low in calories and vitamin E. Coconut milk provides a creamy texture and is rich in healthy fats. Oat milk is a great option for those with nut allergies and contains fibre and beta-glucans, which are beneficial for heart health. Soy milk is a protein-rich alternative that is comparable to dairy milk in terms of taste and texture.
Cultured Dairy-free Buttermilk Alternatives:
For recipes that call for buttermilk, there are also dairy-free alternatives available. Coconut milk buttermilk is made by adding an acid to coconut milk, resulting in a tangy flavour and a similar texture to traditional buttermilk.
Soy milk buttermilk can be made by adding vinegar or lemon juice to soy milk, creating a perfect substitute for baking. Plant-based yoghurts can also be used as a buttermilk alternative by diluting them with water or plant-based milk to achieve the desired consistency.
Popular Myths And Misconceptions
Popular Myths and Misconceptions
Clarifying Common Myths About Milk and Buttermilk. Many people have misconceptions about milk and buttermilk’s health and nutritional benefits. Let’s debunk these myths:
Myth: Milk is unhealthy
Contrary to popular belief, milk is a rich source of essential nutrients such as protein, calcium, and vitamins. It provides support for healthy bones and teeth.
Myth: Buttermilk is fattening
In reality, buttermilk is a low-fat alternative to regular milk. It contains fewer calories and less fat while still offering similar nutritional benefits. It can aid in digestion and provide probiotics.
Myth: Milk causes allergies
Milk allergies are rare, affecting only a small percentage of the population. Most people can safely consume milk without experiencing any adverse reactions. It is important to note that lactose intolerance differs from a milk allergy.
Myth: Buttermilk is sour milk
Buttermilk is not sour milk. It is a cultured dairy product made by fermenting milk with lactic acid bacteria. The tangy taste comes from these bacteria, giving buttermilk its unique flavour.
By dispelling these myths, we can appreciate the health benefits of milk and buttermilk and include them in our diet without hesitation.
Also Read: Oat milk vs Coconut milk: Which is the Better Dairy-Free Alternative?
Allergies And Sensitivities
Allergies and sensitivities, such as lactose intolerance and dairy allergies, can greatly impact individuals when consuming milk and buttermilk. Lactose intolerance, which affects many people worldwide, occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase needed to digest lactose.
However, those who are lactose intolerant might still be able to consume buttermilk. This fermented dairy product contains lower lactose levels than regular milk, making it easier to digest for some individuals.
Dairy allergies, conversely, are immune responses triggered by proteins in milk. These allergies can cause various symptoms, including digestive issues, skin rashes, and respiratory problems. In such cases, milk and buttermilk should be avoided to prevent adverse reactions. Those with allergies must consult a healthcare professional to determine their tolerance to dairy products.
Final Verdict: Inclusion And Moderation
| Final Verdict: Inclusion and Moderation | |
|---|---|
| Subheading: | Making an Informed Choice: Milk or Buttermilk? |
| The Importance of Moderation in Dairy Consumption | |
| Milk is a versatile and widely consumed drink that provides a good balance of nutrients. It contains lactose, a natural sugar found in milk, which can concern individuals with lactose intolerance. On the other hand, buttermilk is a fermented dairy product that is easier to digest for many due to its lower lactose content. | |
| Milk is a versatile and widely consumed drink that provides a good balance of nutrients. It contains lactose, a natural sugar found in milk, which can be a concern for individuals with lactose intolerance. On the other hand, buttermilk is a fermented dairy product that is easier to digest for many due to its lower lactose content. | |
| Making an informed choice between milk and buttermilk is crucial based on individual preferences, dietary needs, and health considerations. Consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help in understanding which option is more suitable for an individual’s specific requirements. The key is to incorporate these dairy products sensibly and in moderation as part of a balanced diet for optimal health benefits. | |
Conclusion
To sum up, milk and buttermilk offer unique benefits and can be incorporated into a healthy diet. While milk is a rich source of essential nutrients like calcium and protein, buttermilk is a lower-calorie option that aids digestion and hydration.
Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on individual preferences and dietary needs. So, next time you’re at the dairy aisle, consider your health goals and taste preferences to make the best choice.
Also Read: