Krill oil and fish oil are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, known for their potential health benefits. Fish oil is extracted from fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, while krill oil comes from tiny marine crustaceans called krill. One of the key differences between them is the form of omega-3s they contain. Krill oil often boasts a higher percentage of phospholipid-bound EPA and DHA, which some believe might lead to better absorption in the body compared to the triglyceride form found in fish oil. Krill oil contains astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant not in significant amounts in fish oil.
While some argue that krill oil may offer superior benefits due to these factors, scientific consensus is still evolving. Both krill oil and fish oil have shown promise in supporting heart and brain health, reducing inflammation, and improving cholesterol levels. Ultimately, the choice between the two may depend on personal preferences, cost considerations, and sustainability concerns, making it crucial to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating either into your diet.
Also Read: Vegetable Oil vs Canola Oil Frying: Which is the Best?
Contents
- 1 What is krill oil?
- 2 What is fish oil?
- 3 Overview Of Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
- 4 Similarities Between Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
- 5 The importance of omega-3 fatty acids for health
- 6 Key differences between krill oil and fish oil
- 7 Potential side effects and considerations Of Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
- 8 Should You Take Krill Oil or Fish Oil?
- 9 Final Comment
What is krill oil?
Krill oil is a dietary supplement derived from krill, which are small, shrimp-like marine crustaceans found in oceans around the world. These tiny creatures are a vital part of the marine food chain and serve as a food source for various marine animals, including whales, seals, and seabirds.
What is fish oil?
Fish Oil is a dietary supplement derived from the tissues of fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies. It is known for its high content of omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are essential nutrients that play important roles in human health.
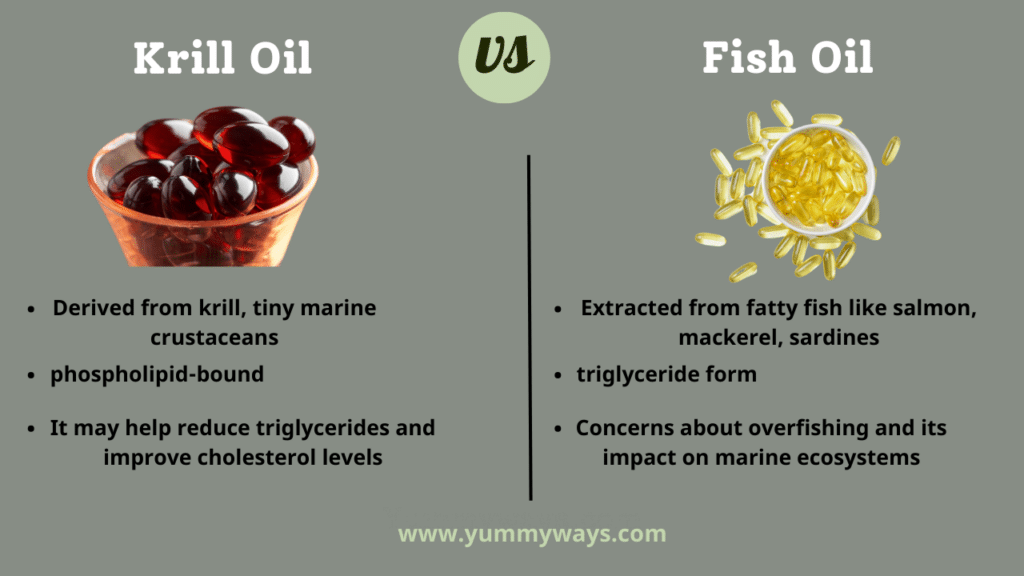
Overview Of Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
| Aspect | Krill Oil | Fish Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from krill, tiny marine crustaceans | Extracted from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | High in EPA and DHA | High in EPA and DHA |
| Form of Omega-3s | phospholipid-bound | triglyceride form |
| Bioavailability | It contains astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant | Absorption may vary among individuals |
| Antioxidant Content | Contains astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant | lacks significant antioxidants |
| Sustainability | It may help reduce triglycerides and improve cholesterol levels | Concerns about overfishing and its impact on marine ecosystems |
| Price | Often more expensive | Varied pricing based on source and brand |
| Heart Health | It may help reduce triglycerides and improve cholesterol levels | May help reduce triglycerides and improve cholesterol levels |
| Brain Health | Supports cognitive function and brain health | Supports cognitive function and brain health |
| Inflammation | Potential anti-inflammatory effects due to astaxanthin | May help reduce inflammation |
| Additional Benefits | Potential benefits of astaxanthin and enhanced bioavailability | It may help reduce inflammation |
| Common Uses | Heart health, joint health, inflammation reduction | Heart health, brain health, inflammation reduction |
| Availability | Readily available as supplements | Readily available as supplements |
Similarities Between Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Both krill oil and fish oil are rich sources of EPA and DHA, essential omega-3 fatty acids with various health benefits.
Heart Health: Both supplements have been associated with improvements in heart health. They can help reduce triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, and support cardiovascular function.
Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA, play a crucial role in brain health and cognitive function. Both krill oil and fish oil can support brain function.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation in the body, making both supplements potentially beneficial for individuals with inflammatory conditions.
Reduced Joint Pain: Some people find relief from joint pain and stiffness when taking krill or fish oil due to their anti-inflammatory effects.
Cholesterol Levels: Both supplements may help improve cholesterol profiles by increasing levels of beneficial HDL cholesterol and reducing levels of harmful LDL cholesterol.
Mood and Mental Health: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids from both sources may positively impact mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
Eye Health: DHA, a component of omega-3 fatty acids, is important for eye health, and both krill oil and fish oil may help protect against certain eye conditions.
Supplement Forms: Krill oil and fish oil are available in various forms, including capsules, liquid, and soft gels, making them convenient to incorporate into one’s daily routine.
Dietary Support: Both supplements can fill dietary gaps in omega-3 intake for individuals who don’t regularly consume fatty fish.
Also Read: Vanilla Essence vs Vanilla Extract: Which One Reigns Supreme in Baking Delights?
The importance of omega-3 fatty acids for health
Omega-3 fatty acids are a crucial group of polyunsaturated fats that play a fundamental role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are several key reasons why omega-3 fatty acids are essential for health:
Heart Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have been extensively studied for cardiovascular benefits. They can help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall heart health. Regular consumption of omega-3s is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
Brain Function: DHA, in particular, is a major component of brain cell membranes and plays a critical role in brain development and function. Adequate intake of omega-3s is essential for cognitive function, memory, and maintaining mental clarity throughout life.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Omega-3 fatty acids have potent anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is linked to various chronic diseases, including arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and heart disease. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially alleviating symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
Eye Health: DHA is also found in high eye retina concentrations. Consuming omega-3s can help support eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and other eye conditions.
Mood and Mental Health: Omega-3s have been associated with improved mood and reduced risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. They are believed to influence the production of neurotransmitters in the brain, which regulate mood.
Joint Health: Omega-3s may help reduce joint pain and stiffness in individuals with inflammatory joint conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. They can alleviate symptoms and improve joint function.
Pregnancy and Infant Development: Adequate omega-3 intake during pregnancy is essential for developing the fetal brain and eyes. DHA, in particular, is important for the infant’s cognitive and visual development.
Skin Health: Omega-3s may help maintain healthy skin by reducing inflammation and preventing skin disorders. They can also promote skin hydration and reduce the risk of eczema.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids may protect against certain types of cancer, although more research is needed to establish a definitive link.
Immune System Support: Omega-3s support the immune system’s function, helping the body fight off infections and maintain overall health.
Key differences between krill oil and fish oil
Krill and fish oil are popular dietary supplements for their high omega-3 fatty acid content, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). These omega-3 fatty acids offer numerous health benefits, but there are important distinctions between the two. Krill oil is sourced from tiny marine crustaceans called krill and contains omega-3s in a phospholipid form, potentially offering better absorption. It also includes the antioxidant astaxanthin. Fish oil, on the other hand, is derived from fatty fish like salmon and contains omega-3s in triglyceride form. While both supplements have demonstrated positive effects on heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation, the choice between krill oil and fish oil often comes down to individual preferences, cost, and sustainability considerations. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine which option aligns best with one’s specific health goals and needs.
Also Read: A Comparative Analysis: Sucralose vs Aspartame
Potential side effects and considerations Of Krill Oil vs Fish Oil
When considering the use of krill oil or fish oil supplements, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects and considerations:
Gastrointestinal Issues: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, or indigestion when taking omega-3 supplements, including krill and fish oil. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it may help minimize these issues.
Fishy Aftertaste and Burping: Fish oil supplements, in particular, can sometimes cause a fishy aftertaste, burping, or an unpleasant odor. Krill oil capsules are often reported to have less of this issue.
Allergic Reactions: While allergies to krill oil are rare, people with shellfish allergies should exercise caution when using krill oil supplements, as they may cause an allergic reaction.
Blood-Thinning Effects: Omega-3 fatty acids, in higher doses, can have a mild blood-thinning effect. This may increase the risk of bleeding, particularly in individuals taking blood-thinning medications or those with bleeding disorders. Consult with a healthcare provider if you’re on anticoagulant medications or have concerns about bleeding risk.
Interaction with Medications: Both krill oil and fish oil supplements can interact with certain medications, such as blood pressure medications, blood thinners, and antiplatelet drugs. You must inform your healthcare provider about any supplements you’re taking to avoid potential interactions.
Sustainability: Consider the environmental impact of your choice. Krill harvesting may raise concerns about the sustainability of marine ecosystems. At the same time, sustainable fishing practices for fatty fish sources of fish oil are essential for maintaining healthy fish populations and ocean ecosystems.
Quality and Purity: Ensure you select high-quality, reputable brands for krill oil and fish oil supplements. Look for products tested for purity, freshness, and the absence of contaminants like heavy metals and PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls).
Dosage: Be mindful of the recommended dosage on the supplement label, and avoid taking excessive amounts without consulting a healthcare professional. Omega-3 requirements can vary based on individual health needs.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult their healthcare provider before using omega-3 supplements, as these fats are essential for fetal and infant development, but excessive intake should be avoided.
Individual Response: Remember that individual responses to krill and fish oils can vary. What works well for one person may not work the same for another. It’s essential to monitor your own health and consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Should You Take Krill Oil or Fish Oil?
Indeed, both krill oil and fish oil are valuable sources of omega-3 fatty acids, each with its own potential health benefits. While some limited research suggests potential advantages of krill oil, such as better absorption and potential heart health benefits, it’s essential to emphasize that these findings are inconclusive, and more comprehensive studies are needed to establish one as definitively superior to the other.
Considering the substantial price difference between the two supplements and the overall body of research supporting the benefits of omega-3s, many individuals may find it practical and cost-effective to supplement with fish oil. Fish oil supplements are widely available, well-studied, and generally more affordable.
However, if it aligns with their health goals and preferences, it could be a reasonable choice for those with the financial means and a particular interest in exploring krill oil’s potential advantages.
Regardless of the supplement chosen, individuals must consult with their healthcare provider if they are taking blood-thinning medications, have a history of blood disorders, or have allergies to fish or shellfish. These factors should be considered to ensure safe and effective supplementation and discuss the appropriate dosage based on individual health needs.
Also Read: Evaporated Milk vs Powdered Milk: Which is Better for Cooking?
Final Comment
Both options offer numerous health benefits when choosing between krill and fish oil. Fish oil is widely available, affordable, and contains higher levels of EPA and DHA. On the other hand, krill oil has higher bioavailability, contains astaxanthin, and is considered more sustainable.
The best choice for you ultimately depends on your preferences, dietary needs, and health goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can also help you make an informed decision based on your circumstances.
Remember, a balanced and varied diet that includes fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and other omega-3-rich foods is also an excellent way to ensure an adequate intake of this essential nutrient.