Gorgonzola and blue cheese are both delicious and creamy varieties of cheese, but they have some differences. Gorgonzola is an Italian cheese with a milder flavour, while blue cheese can have a stronger and more pungent taste. Gorgonzola often has a crumbly texture, while blue cheese is usually creamier. Both cheeses are great for adding a flavorful kick to salads, sandwiches, or pasta dishes. Gorgonzola and blue cheese offer different flavour profiles and textures, making them versatile options for various dishes.
Also Read: Pudding vs Custard: Which Will Satisfy Your Sweet Tooth?
Contents
- 1 Overview Of Gorgonzola vs Blue Cheese
- 2 Gorgonzola vs Blue Cheese: A Delicious Debate
- 3 Conclusion
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 What is the difference between Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
- 4.2 Are Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese made from the same type of mold?
- 4.3 Can I use Gorgonzola as a substitute for Blue Cheese in recipes?
- 4.4 Can I eat Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese if I am lactose intolerant?
- 4.5 Can Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese be frozen?
- 4.6 Are Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese suitable for vegetarians?
- 4.7 Can I use Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese in salads or dressings?
- 4.8 How long can I store Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
- 4.9 Can I eat the rind of Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese?
- 4.10 What are some recommended pairings for Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
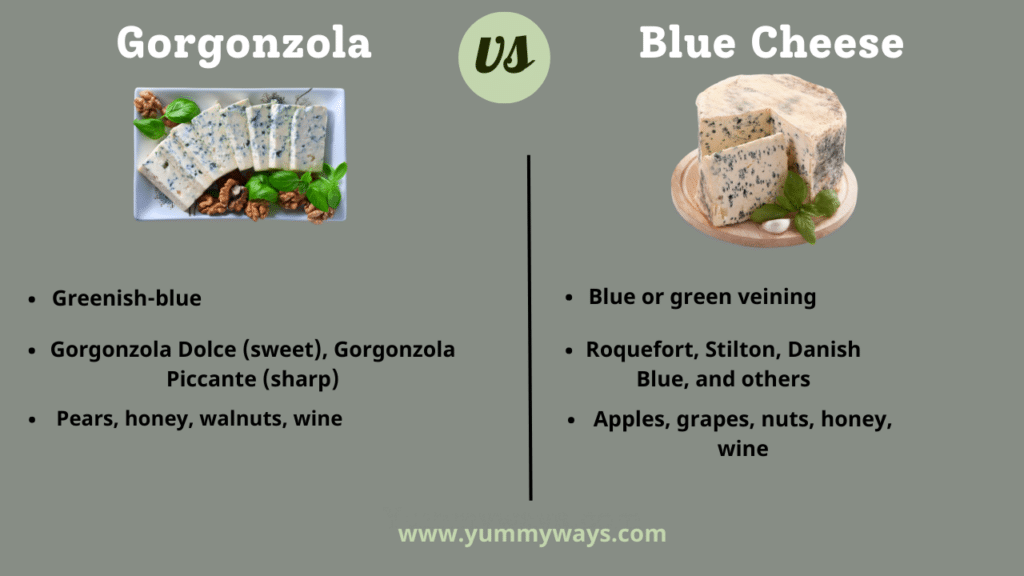
Overview Of Gorgonzola vs Blue Cheese
| Aspect | Gorgonzola Cheese | Blue Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Blue cheese | Blue cheese |
| Origin | Italy | Various regions globally |
| Texture | Creamy, crumbly | Creamy, crumbly |
| Varies, Stilton can be aged longer for a stronger flavor | Strong, tangy | Strong, tangy |
| Veining | Greenish-blue | Blue or green veining |
| Milk Source | Cow’s milk | Cow’s milk |
| Ripening Process | Penicillium mold introduced | Penicillium mold introduced |
| Varieties | Gorgonzola Dolce (sweet), Gorgonzola Piccante (sharp) | Roquefort, Stilton, Danish Blue, and others |
| Culinary Uses | Cheese platters, salads, sauces | Cheese platters, salads, dressings, dips, cooking |
| Pairing | Pears, honey, walnuts, wine | Apples, grapes, nuts, honey, wine |
| Aging | Varies, Dolce is milder, Piccante is aged longer | Varies, Stilton can be aged longer for a stronger flavour |
| Common Dishes | Pasta dishes, risotto, sauces | Salads with blue cheese, steak with blue cheese, blue cheese burgers |
| Global Popularity | Recognized worldwide, especially in Italy | Widely enjoyed globally, various regional variations |
Also Read: Boba vs Tapioca: Decoding the Differences and Making a Choice
Gorgonzola vs Blue Cheese: A Delicious Debate
Regarding gourmet cheese, few varieties can match the rich and complex flavours of Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese. These two popular cheeses have distinct characteristics that set them apart but also share many similarities. This article will explore the differences and similarities between Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese and help you decide which suits your taste buds best.
Origin and History
Gorgonzola hails from Northern Italy, specifically the regions of Lombardy and Piedmont. It has a long history, dating back to the 9th century. Blue Cheese, on the other hand, has a more ambiguous origin, with various countries claiming to be its birthplace. However, it is commonly associated with England and France.
Production Process
The production process for both Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese involves the introduction of specific mold cultures into the cheese. Gorgonzola is made from cow’s milk and is aged for at least 60 days. It undergoes a process known as “penicillium roqueforti” inoculation, which gives the cheese its distinctive blue-green veins.
Blue Cheese, conversely, can be made from cow’s, sheep’s, or goat’s milk. The cheese is pierced with small holes to allow air to enter, promoting mould growth. The aging process varies, with some Blue Cheeses aged for as little as a few weeks while others aged for several months.
Flavour Profile
Gorgonzola is known for its strong and tangy flavour with nutty undertones. It has a creamy and crumbly texture, making it versatile for cooking and as a standalone cheese. The intensity of the flavor can vary depending on the age of the cheese.
Blue Cheese, however, has a bold and pungent flavour, a salty and slightly sweet taste. It has a creamy and smooth texture, with a characteristic marbling of blue or green veins throughout the cheese. Depending on the ageing process, the flavour can range from mild to strong.
Also Read: Food Colouring Gel vs Liquid: What’s the Difference?
Culinary Uses
Both Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese are highly versatile in the kitchen and can be used in various dishes. Due to its stronger flavour, Gorgonzola is often crumbled over salads, melted into pasta sauces, or used as a topping for pizzas. It pairs well with fruits such as pears and figs.
Blue Cheese is a popular choice for salads, dressings, and dips. It can also be melted into creamy sauces, used in sandwiches or burgers, and even incorporated into desserts. Its bold flavour adds a unique twist to any dish.
Nutrition
Both Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese are rich in nutrients. They are excellent sources of calcium, protein, and essential vitamins. However, due to their high-fat content, they should be consumed in moderation.
Pairings
When pairing Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese, there are numerous options to explore. Both cheeses go well with a variety of wines such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Port, or even a sweet dessert wine like Sauternes. They also pair nicely with fruits, nuts, and crusty bread.
Also Read: Sushi vs California Roll: Which is More Authentic?
Conclusion
Whether you prefer the tangy and nutty flavours of Gorgonzola or the bold and pungent taste of Blue Cheese, both varieties offer a delightful culinary experience. Their distinct characteristics and versatile uses make them a staple in many gourmet dishes. So, the next time you want to add a touch of sophistication to your meal, consider indulging in the delicious debate of Gorgonzola vs Blue Cheese.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese are both types of cheese, but they come from different regions and have distinct flavours. Gorgonzola is Italian and has a milder, creamier taste, while Blue Cheese is stronger and more pungent.
Are Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese made from the same type of mold?
Yes, both Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese are made from the same type of mold, Penicillium roqueforti. However, the aging process and other factors contribute to the unique flavours and textures of each cheese.
Can I use Gorgonzola as a substitute for Blue Cheese in recipes?
You can use Gorgonzola as a substitute for Blue Cheese in recipes. However, keep in mind that Gorgonzola has a milder flavor, so it may not provide the same intensity as Blue Cheese.
Can I eat Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese if I am lactose intolerant?
Most people with lactose intolerance can tolerate small amounts of Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese because the aging process reduces lactose content. However, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional with specific dietary concerns.
Can Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese be frozen?
Technically, you can freeze Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese, which may affect the texture and flavour. To preserve the best quality, consuming these cheeses fresh or storing them in the refrigerator for short periods is recommended.
Are Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese suitable for vegetarians?
Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese are suitable for vegetarians as they are made with microbial or vegetarian rennet. However, it’s always important to check the specific brand or consult the packaging for confirmation.
Can I use Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese in salads or dressings?
Yes, Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese can add a delicious and tangy flavour to salads and dressings. Crumble the cheese on top of your salad or whisk it into your dressing for an extra kick of flavour.
How long can I store Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese can be stored in the refrigerator for 2-3 weeks if properly sealed. It’s best to wrap them in wax paper or foil and place them in airtight containers to prevent them from drying out or picking up odours.
Can I eat the rind of Gorgonzola or Blue Cheese?
The rind of Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese is edible, but it may have a stronger and slightly bitter taste. Some people prefer to remove the rind before consuming, while others enjoy it as part of the overall flavour experience.
What are some recommended pairings for Gorgonzola and Blue Cheese?
Gorgonzola pairs well with honey, pears, walnuts, and red wine. Blue Cheese goes well with apples, figs, honey, and port wine. Experiment with different combinations to find your favourite flavour pairings.