Acorns and chestnuts are two fascinating members of the nut family, each offering unique qualities and characteristics. Acorns are the nuts of oak trees, while chestnuts come from the trees of the Castanea genus. On the other hand, chestnuts are renowned for their delicate, sweet flavor and creamy texture. They are associated with autumn and are often roasted, boiled, or used in culinary preparations. Chestnuts are lower in fat and higher in carbohydrates than other nuts, making them an excellent choice for those seeking a satisfying yet healthier alternative.
Some more differences are discussed in the article. The differences between Acorns and chestnuts can help you appreciate the nuances of these two classic dishes. We will also discuss the similarity and many more queries about them. So, let’s explore what makes Acorns and chestnuts so special!
Contents
- 1 What are Acorns?
- 2 What are Chestnuts?
- 3 Overview Of Acorns vs Chestnuts
- 4 Detailed Differences Between Acorns vs Chestnuts
- 5 Which One is Better?
- 6 Conclusion
- 6.1 What are acorns and chestnuts?
- 6.2 How do acorns and chestnuts differ in appearance?
- 6.3 Are acorns and chestnuts edible?
- 6.4 Which nut, acorn or chestnut, is more used in culinary traditions?
- 6.5 Can acorns and chestnuts forage in the wild?
- 6.6 Are there any environmental considerations when harvesting acorns and chestnuts?
What are Acorns?
Acorns are the nuts produced by oak trees. They are small, round, or oval-shaped and have a hard outer shell. Inside the shell is a single seed known as the acorn kernel. Acorns come in various sizes and colors, depending on the oak tree species. Also Read: Beets vs Turnips: A Comprehensive Comparison
What are Chestnuts?
Chestnuts are a type of nut that comes from trees in the genus Castanea. They are native to the Northern Hemisphere’s temperate regions, including Europe, Asia, and North America. Chestnuts have been an important food source for thousands of years and are known for their distinctive flavor and texture.
Overview Of Acorns vs Chestnuts
| Characteristics | Acorns | Chestnuts |
| Tree Species | Oaks (Genus: Quercus) | Chestnuts (Genus: Castanea) |
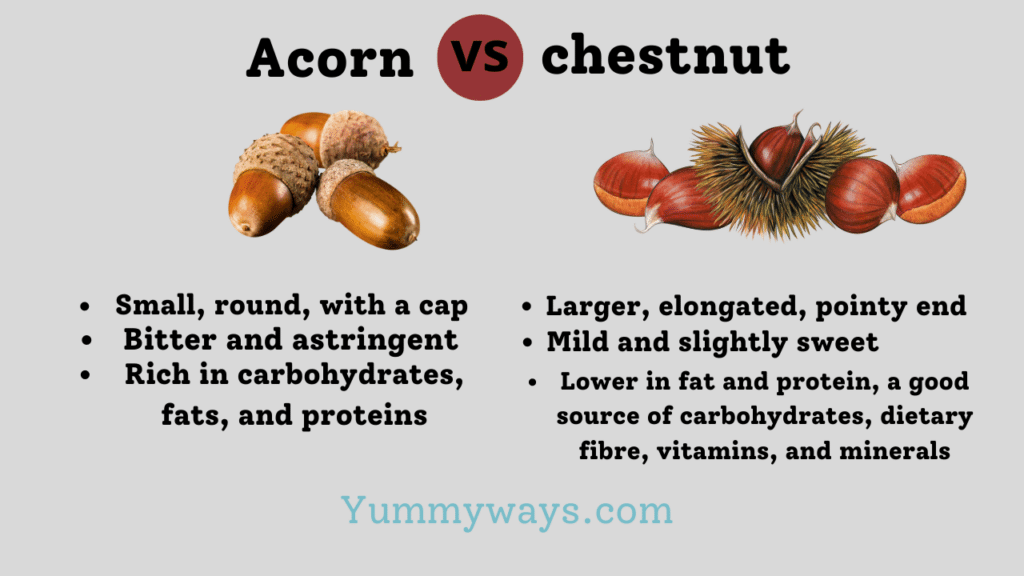
| Appearance | Small, round, with a cap | Larger, elongated, pointy end |
| Taste | Bitter and astringent | Mild and slightly sweet |
| Culinary Use | Limited, often processed | Widely used in cooking |
| Nutritional Profile | Rich in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins | Lower in fat and protein, a good source of carbohydrates, dietary fibre, vitamins, and minerals |
| Preparation | Typically require processing to remove tannins | Roasted, boiled, steamed, or used in various dishes |
| Culinary Applications | Not commonly used in human cooking | Roasted, boiled, and used in stuffings, soups, desserts, etc. |
| Availability | Abundant in oak forests | Cultivat |
Detailed Differences Between Acorns vs Chestnuts
Acorns and chestnuts are both types of nuts, but they come from different trees and have some distinct differences. Here are some detailed differences between acorns and chestnuts:
Tree Species
Acorns are the nuts produced by oak trees, which belong to the genus Quercus. Over 400 species of oak trees worldwide, each producing slightly different acorns.
Chestnuts come from trees belonging to the genus Castanea. The most common species is the European chestnut, but other species, like the American and Chinese chestnuts, exist.
Appearance
Acorns are small, rounded nuts with a cap at the top. They are brown in color, but the shade can vary depending on the oak species.
Chestnuts are larger than acorns and have a more elongated shape. They are light to dark brown and have a smooth, glossy outer shell.
Nutritional Composition
Acorns are high in fat and carbohydrates. They are also a good source of protein, fiber, and minerals such as potassium, phosphorus, and calcium. However, acorns also contain a lot of tannins, which are bitter and must be removed or leached before consumption.
Chestnuts are relatively low in fat and protein compared to other nuts. They are high in carbohydrates, mainly starch. Chestnuts are a good source of dietary fiber, vitamin C, and minerals such as potassium and magnesium.
Culinary Use
Acorns have been traditionally used as a food source by indigenous cultures in various parts of the world. However, due to their high tannin content, acorns must be processed before consumption. The tannins can be removed by leaching, grinding, or roasting. Acorns are ground into flour and used in bread, cakes, and porridge recipes.
Chestnuts are widely used in cooking and have a sweeter flavor than acorns. They are eaten raw but are roasted, boiled, or used in various culinary preparations. Roasted chestnuts are a popular snack during the winter season in many countries. They are also used in desserts, stuffing, soups, and stews.
Cultural Significance
Acorns have cultural significance in several societies. They have been used as a food source and also hold symbolic value. In some Native American cultures, acorns are considered sacred and used in religious ceremonies and as a dietary staple.
Chestnuts have cultural importance in many regions, especially in Europe and Asia. They are associated with autumn and are often linked to festive occasions and traditional dishes. In some European countries, like Italy, roasted chestnuts are a common street food during the colder months.
Which One is Better?
When it comes to comparing acorns and chestnuts, I have a slight preference for chestnuts. I find something about their sweet and creamy taste delightful. Whether raw or cooked, chestnuts satisfy my cravings for a delectable snack.
From a nutritional standpoint, chestnuts offer several benefits. They are lower in fat and calories than acorns, making them a guilt-free option. Chestnuts are a great source of dietary fiber, vitamin C, and essential minerals like potassium and magnesium, contributing to a well-rounded and healthy diet.
In terms of culinary versatility, chestnuts take the lead for me. I love roasting them and relishing their irresistible aroma and flavor. They can be enjoyed as a delightful snack or incorporated into various dishes such as stuffing, soups, or desserts, adding a unique twist to the recipe.
Another aspect that sways me toward chestnuts is their widespread availability. I can easily find them in local markets or grocery stores throughout the year, making them convenient for enjoying their delightful taste whenever desired.
While acorns have their appeal with their nutty flavor, they often require additional processing to remove bitter tannins. This extra step is time-consuming and diminishes my enthusiasm for using acorns in culinary endeavors. Furthermore, it’s worth mentioning that some species of acorns contain tannins that can be toxic if consumed in large quantities or without proper processing. This aspect adds caution and effort when considering acorns as a food source.
Chestnuts are my superior choice considering their taste, nutritional value, culinary uses, and availability. Their sweet and creamy flavor and nutritional benefits make them an irresistible option I thoroughly enjoy.
Conclusion
Both acorns and chestnuts have their unique nutritional benefits and taste profiles. Ultimately, the choice between the two comes from personal preference and intended use. Chestnuts are a great vitamin C and fiber source, while acorns are high in healthy fats and protein. Chestnuts are also sweeter and more versatile in cooking, while acorns require more preparation to reduce their bitterness. So, whether you prefer the sweet and versatile chestnut or the nutrient-dense acorn, both nuts are a healthy and delicious addition to your diet.
What are acorns and chestnuts?
Acorns and chestnuts are types of nuts that come from different tree species. Acorns are the nuts of oak trees, while chestnuts come from chestnut trees.
How do acorns and chestnuts differ in appearance?
Acorns are small and round, with a cap covering the top part of the nut. They have a brown color and a smooth texture. Chestnuts, on the other hand, are larger and have a distinct pointed end. They are enclosed in a spiky shell called a burr and have a shiny brown color.
Are acorns and chestnuts edible?
While both acorns and chestnuts are edible, there are some differences in their taste and preparation. Chestnuts are sweet and nutty and are consumed roasted or boiled. On the other hand, Acorns contain high levels of tannins that make them bitter and inedible when raw. However, acorns can be processed to remove the tannins and used in cooking.
Which nut, acorn or chestnut, is more used in culinary traditions?
Chestnuts have a long history of culinary use in various cultures worldwide. They are particularly popular in European and Asian cuisines. Acorns, on the other hand, have been historically used as a food source by indigenous peoples in certain regions, but they are less commonly used in mainstream culinary traditions.
Can acorns and chestnuts forage in the wild?
Yes, both acorns and chestnuts can be foraged in the wild. Chestnuts are found in chestnut tree groves, while acorns can be gathered from various oak tree species. However, it’s important to have proper knowledge and identification skills before foraging for nuts in the wild to ensure safety and avoid toxic species.
Are there any environmental considerations when harvesting acorns and chestnuts?
When harvesting acorns and chestnuts, it’s important to do so sustainably and with respect for the environment. Avoid over-harvesting from a single tree or location, as it can negatively impact local wildlife that relies on these nuts as a food source.

